Description of Types of Surgical Scar Revision
Listed below are the most common surgical techniques utilized in scar revision.
Z-plasty is a reconstructive surgery procedure. Its utilization is for improving the functional and aesthetics of scars. Functionally refers to the lengthening of the scar the lengthening of a scar which helps relax or release linear burn scar contractures. The availability of mobile adjacent skin is a predicator for the use of this medical procedure. Z-plasty can procedurally make the scar less noticeable. Re-alignment of the central element can place the scar in natural skin tension lines and thereby disguise it. Utilizing this procedure the surgeon can rotate the tension line of a scar and or make a contracted scar elongated. In Z-plasty the midline of the Z-shaped incision is made along the meridian of highest tension or contracture. Triangular flaps are raised on the opposite ends of this incision. The flaps are than transposed and closed.
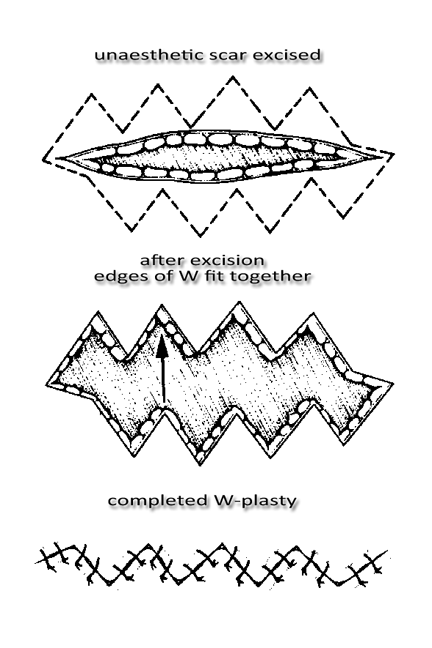
W-plasty is another reconstructive plastic surgery technique used for the excision of unaesthetic scarring. The excised edges of the scar are cut in a zig-zag pattern is like a connected row W’s. The borders are interdigitated for suturing. This method is very effective in rendering a linear scar irregular and less visible.
W-plasty revisions the scar into a ‘pinking shear pattern; which will interlock when sutured. Optically, it is more difficult for the eye to follow an irregular line. This makes W-plasty a favored method for revisioning linear scars. Often there is no discreet skinfold to hide a scar. Think of areas such as the forehead, the side of the face or cheek. Still is the irregular pattern is uniform visibility is not obscured. For that reason W-plasty is most often combined with
Geometric Broken Line Closure (GBLC).
W-plasties are not usually employed on their own throughout the entire scar. Visibility of the scar can be better reduced by combining other patterns with the W pattern. This is a more sophisticated procedural technique of scar revision is known as geometric broken line closure (GBLC). W-plasty is the basic technique and then other shapes besides triangular flaps are utilized for interdigitation creating a very irregular irregularity. This procedure offers the optimal potential for camouflaging the scar. Added to this is also dermabrasion which is done approximately two to three months after the surgery.
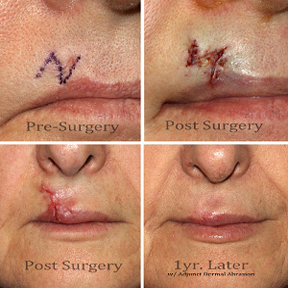
M-plasty
The object of electing M-plasty in reconstructive surgery is to better preserve healthy tissue and to reduce the chance of secondary tissue deformity. Proper technique in M-plasty reduces the loss of surrounding health tissue by nearly fifty percent. The M-plasty is performed by creating two separate thirty degree angles instead of a single one.
Adjunctive Techniques of Scar Revision
Dermabrasion
- precisely and in a controlled deliberate manner superficial abrading of the scar and surrounding skin. The end result is a smooth texture and in some cases further reduced visibility.
- Abrasion can be used in a process that will improve the appearance of uneven scar edges including: scar edges, grafts and or flaps.
- Dermabrasion works best on lighter complexions because of the lower risk of dyspigmentation.
Intralesional Steroids
- Hypertrophic linear scars, bulky grafts and flaps, can be treated with intralesional corticosteroids. Injections can be instituted at approximately 1 month postoperatively.
- A small amount (as little as 0.1 mL) of low-dose triamcinolone acetonide at 5 to 10 mg/mL is injected into the scar; this dosage can be repeated monthly until the scar has flattened.
- Side effects include atrophy (if the injection leaks out into healthy skin ), hypopigmentation and telangiectasias when injected in higher concentrations into the dermis.
Contraindications
The reasons for a patient not to undergo scar revision include:
- The present psychological status of the patient does not prepare the patient for a positive outcome.
- The patient’s expectations are unrealistic limiting the opportunity for a favorable visible outcome.
- An individual’s history for hypertrophic and or keloid scarring represent a poor risk for a pleasing aesthetic result.
- Patient’s with thickened skin from the trauma reducing compliancy endure the risk of a compromised scar revision.