Traumatic Injures of War
A young child in Mosul, Iraq is playing in a war torn neighborhood. Chasing a ball made of newspaper in tape she inadvertently steps on an IED. Outside Kabul a coalition humanitarian worker and a soldier a bring aid to an Afghan family. There vehicle hits a landmine they are severely burned and scarred from burns and loss of muscle. New technology promise hope for such victims.
University of Pittsburgh doctors have helped a soldier injured in Afghanistan regrow muscle to restore his strength and range of motion in his severely injured leg. McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine, at the University of Pittsburgh is headed by Stephen Badylak, doctors there are pioneering cutting edged treatments for recovery of traumatic battlefield wounds. These injuries include burns and blast injuries. These amazing treatments include wound healing, craniofacial reconstruction, and limb regeneration.
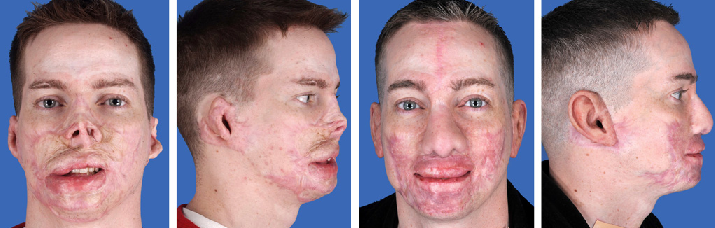
A new therapy developed at the institute is called the “skin gun.” It is actually a spraying device used to spray wounded areas with skin cells over burns on the ears and face. Skin can regrow over the affected burn areas in just a matter of days. The Bioreactor Group is under the direction of Professor Joerg Gerlach, they are the developers of this exciting restorative treatment.
There are three innovative treatment programs headed by the McGowan medical team. Extensive research on biominerlization (scaffolding) and bioceramic nanoparticles in non-viral DNA gene delivery. Professor Charles Sefeir leads the studies focused on the role of extracellular matrix in tissue engineering and biominerliazation.
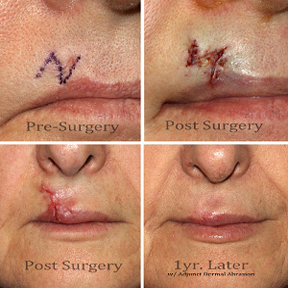
One of the most critical areas of the centers work is the reconstruction of soldiers’ faces with the most normal looking appearance as possible for the patients. A cross functional team led by Professor J. Peter Rubin coordinate their complimentary expertise to bring about positive results with the advancement medical treatments of the McGowan Institute.