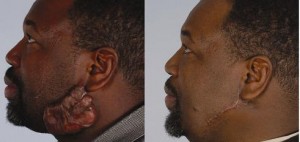
According to American Osteopathic College of Dermatology, a keloid is scar tissue protruding from the skin at the site of an injury. It is caused by fibroblasts (connective tissues) being overactive in the healing process and producing extra tissue. Some people are genetically prone to keloid formation and people with dark skin types are often more at risk, notes the NHS website. For these people, skin damage as small as a pimple or piercing can cause keloid formation.
Step 1
Apply steroid-impregnated tape to the injury site. If you are at risk of developing keloids, preempt their development by applying a dressing doused in a natural steroid like cortisone to the wound for 12 hours a day, notes the NHS website. Alternatively, AOCD notes, use a pressure dressing pad or tape containing silicone gel and where for 24 a day. This also can stop the development of keloids.
Microskin for Scars Helps Cover Up Scars Instantly! Waterproof, No Rub Off, Last Days. www.microskincenter.com
Sponsored Links
Step 2
Schedule an appointment with your dermatologist to discuss laser treatment for the keloid scar. A heated laser can help reduce skin redness and improve texture of the skin, according to AOCD, but it will not help flatten out the keloid in any way.
Step 3
Consult your dermatologist about a method called cryosurgery to help reduce the keloid. This involves freezing the scar with liquid nitrogen and subsequently stopping the swelling. It can be applied via cotton ball and sprayer. It is good for use on new and small keloids as it can prevent them growing further, notes AOCD. As Acne.org notes, the liquid nitrogen can also cause the scar tissue to die completely, allowing for removal.
Step 4
Get cortisone injection treatment for your keloid scars. This natural steroid is a corticosteroid produced in the adrenal glands of the body and is said to help reduce swelling and inflammation, notes Acne.org. AOCD advises to inject the cortisone directly into the keloid once a month. A noticeable flattening of the scar may begin to occur within three to six months.
Step 5
Attempt to remove the keloid via surgery. In the most extreme cases, the keloid can be sloughed off, then the site exposed to electron beam and orthovoltage radiations to prevent any regrowth. AOCD states that exposing the wound to X-rays has stopped regrowth in 85 percent of cases.