Anyone who has ever experienced some form of trauma on their body knows it takes proper aftercare to keep the impacted area from getting infected or developing a scar (including a keloid scar). Patients who are not sure what causes a keloid scar, or how to prevent them, should read this informative article to get the inside scoop on keloid scars and how to get rid of them.
Keloid Scars – What are They?
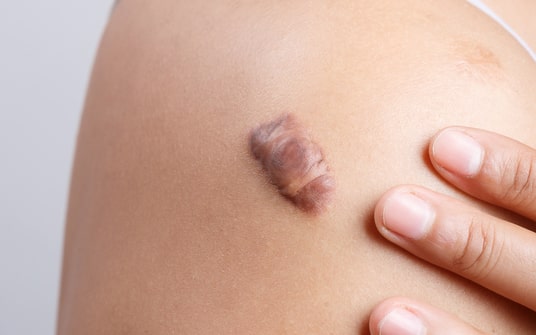
In general, a keloid scar can be defined as an overgrowth of scar tissue that often spreads outside the boundaries of the original scar or injury to the body. Keloid scars are often visible as itchy, firm and/or painful bumps that are present at the site of an earlier injury to the skin. The earlier injury can be some form of trauma to the body as well as a piercing or lesion that is located on the body.
It should be noted that it takes some time for keloids to form on the body. They tend to take anywhere from three to six months to appear and these scars normally begin as a raised scar that is located on the surface of the skin. The keloid scar tends to grow slowly.
It is also important to realize that keloid scars should not be confused with other raised scars. Overall, keloid scars have around three times more collagen than raised, thick scars that are known as hypertrophic scars.
Keloid Scars – Who Can Get Them and Why?
While almost anyone can develop a keloid scar, there are some factors that can increase the chances of one developing on the body. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, “About one-third of people who get keloids have a first-degree blood relative (mother, father, sister, brother, or child) who gets keloids. This family trait is most common in people of African or Asian descent.”
It is also recommended that people who are at a higher risk of developing keloids avoid having an elective procedure on an area of the body that is known for keloid formation (such as the chest and upper back). Even though keloids most often occur after a scar, there are also “spontaneous keloids” that can appear on skin that has not been injured. This most often happens to people who have a history of keloid formation, in their family or a personal experience, and it is highly likely that more than one keloid will present at the same time.
At the moment, it is not clear which mechanisms in the body cause some people to develop a scar in this manner. However, research has indicated that chronic inflammation can play a part in their formation.
Keloid Scars – How to Prevent Them from Forming
The ability to prevent keloid scars is difficult since there is not a lot of information on why some people get them and others do not after an injury. While there is not anything that can be done to prevent the occurrence of spontaneous keloids, there are some steps that can be taken to try and minimize the growth of these scars soon after an injury.
Proper wound care should be performed in order to prevent an infection. In addition, a scar sheet that is silicone-based should be applied as soon as possible to the wounded area on the body. In addition, the massaging of the scar tissue using a silicone gel is also helpful when trying to prevent a keloid scar from forming. If an ear piercing shows the skin in the piercing area is starting to thicken, the piercing should be removed and then replaced with a pressure earring.
Keloid Scars – Getting Rid of Them
There are some suggestions for home remedies to heal keloids, but the best advice is to schedule an appointment with a medical professional who is experienced in treating this condition.
For example, many dermatologists offer steroid injections that, after multiple treatments, can decrease the amount of thickness of keloid scars. Plus, laser and light-based therapies such as CO2 lasers and LED light therapies have been shown to improve their appearance.
If someone thinks they have a keloid or they are afraid that one is going to occur, the patient should consult with a dermatologist in order to address the issue with proper medical treatment. It is hard to predict when they will happen, and it is also hard to sometimes determine the extent of the keloid scar. An experienced doctor can examine the impacted area in order to determine the best course of action in treating the scarring.
There have even been some instances where resistant keloids have been treated via intralesional treatments with surgery, off-label chemotherapy products and radiation therapy to address the issue. These are
serious treatment options that need to be discussed with a medical professional before a final decision is made about utilizing them to address the keloid scarring on the skin.

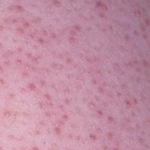 Keratosis pilaris is not harmful, so medical treatment is not necessary. However, scarring may occur as a result of this condition, so it is recommended to exfoliate with a mild soap and moisturize skin at least twice a day. Over-the-counter creams and lotions are what most people use to treat this condition. The effectiveness of these creams is very limited. There have been a few cases that it was treated by laser therapy, however research is still being done to find out the best treatment for this condition.
Keratosis pilaris is not harmful, so medical treatment is not necessary. However, scarring may occur as a result of this condition, so it is recommended to exfoliate with a mild soap and moisturize skin at least twice a day. Over-the-counter creams and lotions are what most people use to treat this condition. The effectiveness of these creams is very limited. There have been a few cases that it was treated by laser therapy, however research is still being done to find out the best treatment for this condition.