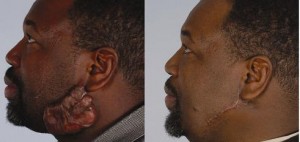
People often wonder what their scar is going to look like after surgery. Surgeons can give a general idea of the size, color and appearance of the scar but each person heals differently. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), scar tissue is usually thicker than the surrounding skin as well as pink or red in color. However, the appearance of a scar largely depends on the size and depth of the wound. Also, the age of the patient, location of the wound and the time it takes for the wound to heal are all aspects which can influence the look of the scar.
Understanding Scar Tissue
 After surgery, the body uses its ability to create scar tissue to heal the new wound. However, excess scar tissue beneath the skin can be troubling even after the wound has healed. The tough, fibrous tissue can cause pain and significantly reduce function or range of motion. This decrease in function may transpire due to the direction of the incision and/or the depth of the wound.
After surgery, the body uses its ability to create scar tissue to heal the new wound. However, excess scar tissue beneath the skin can be troubling even after the wound has healed. The tough, fibrous tissue can cause pain and significantly reduce function or range of motion. This decrease in function may transpire due to the direction of the incision and/or the depth of the wound.
For example, bend and straighten the elbow. The folds that form in the skin are known as Langer’s lines. These lines characterize the direction and orientation of the collagen fibers. While making an incision parallel with the Langer lines can happen in some cases, it is not always possible. This is because most surgeries involve cutting into multiple layers of the anatomy. Each layer that is severed must be repaired. As the collagen fibers begin to rebuild, they tend to be erratic and can cause a tightening which can impede some functions. Likewise, surgery on the knees, wrists, shoulder or ankles is often meant to improve movement and function but scar tissue that forms around the joints can create the opposite effect. Frozen shoulder, a condition some patients experience after surgery, is a buildup of scar tissue around the shoulder joints that can cause irritation and inflammation. This can lead to post-surgical pain and impair the range of motion.
Abdominal and Pelvic Adhesions
Abdominal incisions, such as when a person has their appendix removed, can cause abdominal adhesions. Adhesions are bands of tissue which form between the abdominal tissues and the organs. These bands often cause the usual slippery internal tissues and organs to stick together. This can lead to a twisting and pulling of the small or large intestines which create bowel obstruction and chronic pain. Likewise, pelvic adhesions can form after gynecological surgery and cause pain and infertility in some cases. Using certain surgical techniques, such as creating adhesion barriers, can help reduce these pelvic adhesions. Therefore, patients are encouraged to ask their surgeon how they plan to minimize the risk of adhesions.
Scar Prevention and Treatment
Prior to any surgery, patients should ask how much scarring is expected and what type of preventative treatment is recommended. Anytime the patient is undergoing a procedure that involves surgically manipulating a joint area, the surgeon will recommend moving the joints immediately after surgery. This improves function and also helps to prevent excess scar tissue from forming. Patients are always advised to follow post-surgical recommendations and perform targeted exercises to help stretch the skin and guide joints back into the proper position. Massage therapy and ultrasound therapy may also be used to help soften scars and maintain motion after surgery. Although these scar prevention treatments can help to eliminate an accumulation of scar tissue in many patients, some people still develop debilitating scar tissue. Nevertheless, there are numerous scar treatment options which can improve or lessen the appearance of scars and help patients regain motion.
SP