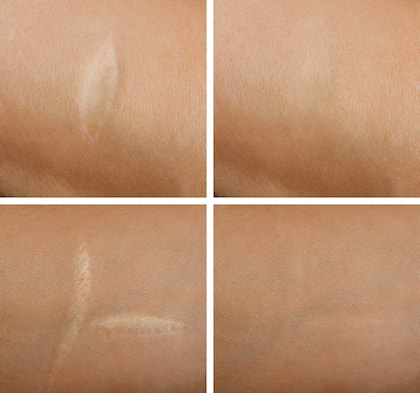
Everyone has scars but they often react differently to having them on the body. Some consider their scars to be cool and something to be proud of while others are embarrassed and want to hide them from the view of others. Whether you are self-conscious about your scars or do not mind displaying them, the fact is many people seek treatment to try and get rid of them. Almost everyone would want to reduce or remove a scar, but they need to understand what a scar really is and the way to approach removing them.
Scars – How do They Form?
A scar is formed due to the natural healing process of the body after an injury. The layer of skin known as the dermis forms collagen fibers to repair any damage done to it. The formation of those fibers results in your scar. Most scars follow the rule of the faster the wound heals, the less collagen fibers there will be, which means a less noticeable scar. To go along with this, the severity of the scar is usually dependent on the severity of the injury to the body. There is also the variable of how scars form differently based on different parts of the body and based on the age of the injured person.
Types of Scars
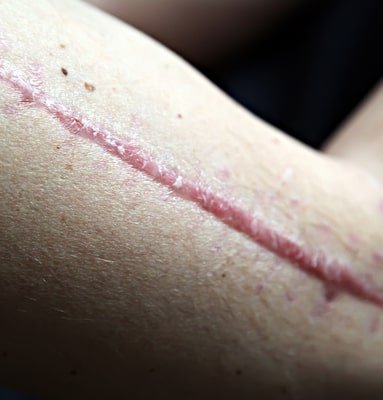 Atrophic scars are defined by the loss of tissue on the skin of the injured person. They can appear in different ways including depressed or flat against the upper layer of the skin. If you see a scar with darker skin pigmentation than other areas of the skin, it might be an atrophic scar. A couple of examples of atrophic scars are acne scars and chickenpox scars.
Atrophic scars are defined by the loss of tissue on the skin of the injured person. They can appear in different ways including depressed or flat against the upper layer of the skin. If you see a scar with darker skin pigmentation than other areas of the skin, it might be an atrophic scar. A couple of examples of atrophic scars are acne scars and chickenpox scars.- Hypertrophic scars can be identified by excess tissue that forms over the injured skin as it heals. As with an atrophic scar, hypertrophic scars are typically darker than the other skin in the surrounding area of the body.
- Keloid scars, like hypertrophic scars, involve too much tissue formation. Keloid scars are what happens when aggressive healing causes an overproduction of tissue. They can be identified by a thick, puffy, or raised appearance and are normally darker than the pigment in the surrounding area. One of the unique things about a keloid scar is that it can grow beyond the initial injured area of the body.
- Contracture scars are most commonly formed after suffering burns on the body. They involve lots of areas of the skin being damaged or lost completely. They can be identified by shiny, tight skin that can restrict movement in the injured part of the body.
Top Four Easy Fixes for Scars
 Scars will become naturally lighter over time, but they will never fully disappear. However, there are many efficient treatments to help speed up the healing process. The following four remedies have helped people in making their scars less noticeable:
Scars will become naturally lighter over time, but they will never fully disappear. However, there are many efficient treatments to help speed up the healing process. The following four remedies have helped people in making their scars less noticeable:
- Aloe vera should be applied directly to the scar, using circular motions, after removing the dark green “skin” from the flat side of the aloe vera leaf and scooping out the light green gel. Once 30 minutes goes by, remove the gel by washing it off with cool water. Patients should repeat this process twice each day.
- Vitamin E should come in a capsule so cut open the capsule and squeeze the Vitamin E oil onto the scar. Massage the oil on, and around, the area of the injured skin/scar for about ten minutes. After this, wait approximately 20 minutes and wash off the oil with warm water. Patients should repeat this whole process a minimum of three times a day.
- Believe it or not, a household potato can help treat the appearance of scars. First, slice the potato into medium-sized rounds and then rub the potato slice on the scar in light, circular motions. The potato slice will eventually dry out. When it does, simply throw it away and continue with another slice. Continue the rubbing for about 20 minutes and then let the scar “air-dry” for about 10 minutes. Finally, wash the injured area with cool water. This process should be performed at least one time per day.
- Another easy household item that can be used on scars is baking soda. For this technique, mix distilled water into two tablespoons of baking soda until it forms a paste. Wet the injured area with the distilled water and then rub the paste on top of the wet scar. Hold the paste on the scar continuously for about 15 minutes and then rinse the area surrounding the scar. This process should be performed once per day.
Scars and Natural Remedies
Natural remedies are a great way to make a scar look less noticeable in an easy, efficient, and healthy way. Many experts believe in the healing power of natural remedies. They also recommend having a conversation with a board-certified doctor before attempting to perform home remedies.

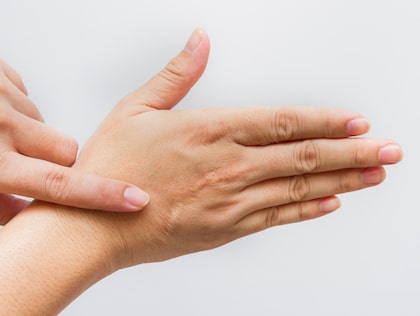 Scar revision surgery is performed to minimize the look of a scar as well as help the scar better blend-in with the skin that surrounds it. Scars can be the result of a surgical procedure and they can also appear after an injury or accident occurs to a person. Once an injury or wound appears on the skin, the soft tissues that surround the wound or injury can change shape or become uneven, sunken or
Scar revision surgery is performed to minimize the look of a scar as well as help the scar better blend-in with the skin that surrounds it. Scars can be the result of a surgical procedure and they can also appear after an injury or accident occurs to a person. Once an injury or wound appears on the skin, the soft tissues that surround the wound or injury can change shape or become uneven, sunken or 
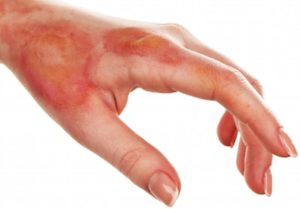 First-Degree Burn – The burn only damages the epidermis of the skin (top layer of the skin) and causes skin discoloration that is pink to red. In addition, the skin will show some minimal swelling and patients will experience some moderate discomfort but the burn can normally be treated at home.
First-Degree Burn – The burn only damages the epidermis of the skin (top layer of the skin) and causes skin discoloration that is pink to red. In addition, the skin will show some minimal swelling and patients will experience some moderate discomfort but the burn can normally be treated at home.