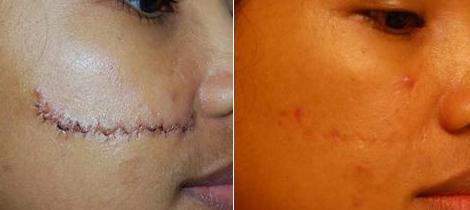
FUE hair restoration can reduce scars
Modern hair transplant is resolving hair loss issues for many people. However the most common form of Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) surgery ‘Strip Method’ procedure leaves a linear scar that is just not acceptable. This lends to the increasing popularity of Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair restoration surgeries.
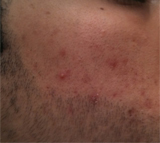
FUE varies from the other FUT procedure by the method of extracting, or “harvesting,” donor hair. An FUE procedure involves the use of an instrument is to make a small, circular incision in the skin around a follicular unit, separating it from the surrounding tissue. The unit is then extracted (pulled) directly from the scalp, leaving a small wound.
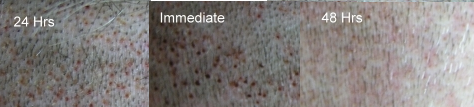
This process is repeated until the hair transplant surgeon has harvested enough follicular units for the planned hair restoration. This nature of this process means it takes o time to complete the procedure. This of course varies under the number of grafts being extracted. The donor wounds are approximately 1-mm in size and in most cases heal within a week to ten days.
Patients can be concerned about the punctuate scars from FUE but in most cases they become undetectable in a short period of time.
Scars from FUE vary do to:
1. The size of the punch (ranges of punch sizes are from 0.8-1.5mm)
2. The density of the donor hair area; the thicker the hair the less visible the scars
3. The inverse is true; the thinner the donor hair the more visible the scare
4. The individual patients healing
Hypopigmentation
Generally, the donor area appears to heal without visible scarring. In some instances a patient can experience loss of color in the donor extraction wounds. These tiny spaces that lack the same degree of scalp colorization than the surrounding donor area. This is more apparent if the patient has darker skin. A hair transplant surgeon can test with a few test extractions prior to committing to a full surgery.


 When an imbalance occurs between the anabolic and catabolic phases of the healing process in a wound somtimes more collagen is produced than the is degradation of collagen in the healing process. This results in the scar growing in all directions. The scar is elevated above the skin and remains hyperemic. This is excessive scar tissue is medically classified either as a keloid or a hypertrophic scar.
When an imbalance occurs between the anabolic and catabolic phases of the healing process in a wound somtimes more collagen is produced than the is degradation of collagen in the healing process. This results in the scar growing in all directions. The scar is elevated above the skin and remains hyperemic. This is excessive scar tissue is medically classified either as a keloid or a hypertrophic scar.