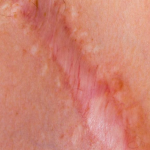
 Scarring is the result of tissue fibers replacing normal skin after a trauma. Scarring can result from surgery, burns, open wounds, or any other abrasion of the skin. Scars are caused when the deep thick layer of skin, also known as the dermis, is damaged. Once trauma occurs, the body forms a collagen fiber which aids in the healing process of the wound and causes a scar. Because the tissue is a different consistency and quality the scar becomes visible.
Scarring is the result of tissue fibers replacing normal skin after a trauma. Scarring can result from surgery, burns, open wounds, or any other abrasion of the skin. Scars are caused when the deep thick layer of skin, also known as the dermis, is damaged. Once trauma occurs, the body forms a collagen fiber which aids in the healing process of the wound and causes a scar. Because the tissue is a different consistency and quality the scar becomes visible.
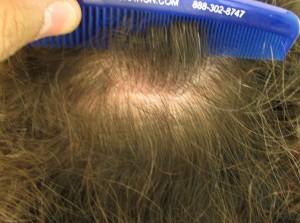
Some scars can be easily hidden, while other will always be visible. Even though scars can never be removed completely, there are procedures offered that will improve the appearance of the scar. Laser resurfacing can be used to remove the surface layers of the skin, resulting in a less visible scar. If a person has a larger scar, surgery is an available option to reduce the size of the scar. Scalp Micro Pigmentation is a new method being offered which uses dermal pigments to camouflage the scars on hair bearing areas of the scalp or face.
If a scar leaves an indentation in the skin, you can use filler injections to raise the scar to the level of the surrounding skin. This type of treatment will be temporary, meaning it should be done a few times a year. If you have a keloid scar, scars that are raised, steroid injections can help flatten the scar giving it an enhanced appearance.
To reduce heavy scarring, topical creams and ointments can be used directly after trauma. Certain scars will fade away after a year and will not need any special method of treatment. For all other cases, it is best to see a specialist who can further assist you.

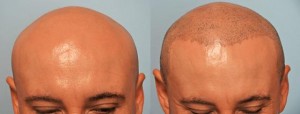
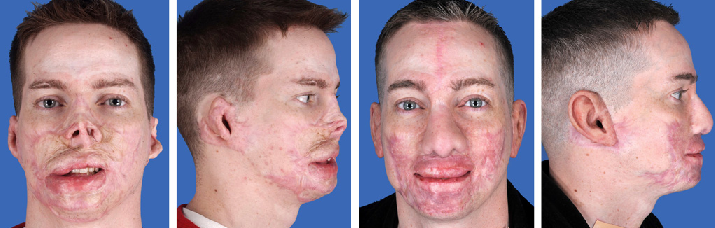
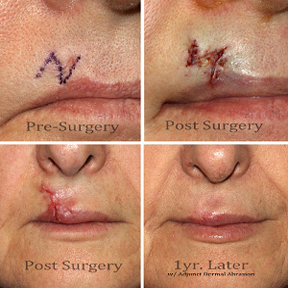
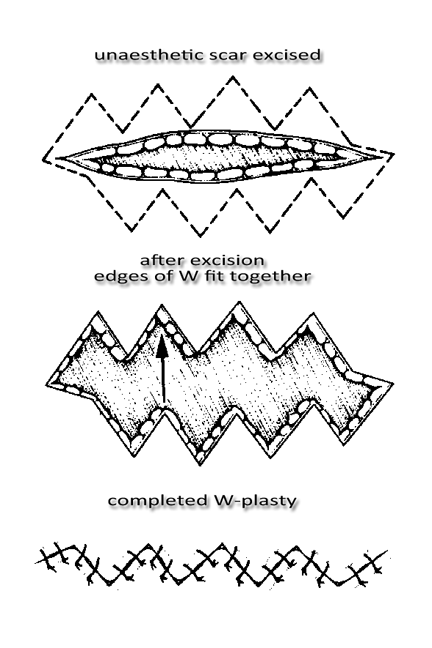
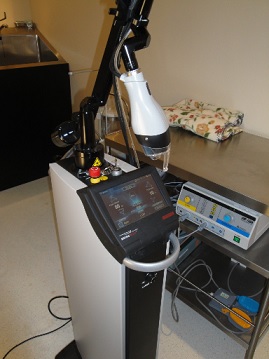 Scars are immensely varied and come in all shapes and sizes. Surgery remains the best option for more severe scars, other scars can be treated with the advance development of lasers for dermatological use. Treatment of scars with laser has steadily grown, giving both patients and physicians more flexibility to determine the best method of treatment.
Scars are immensely varied and come in all shapes and sizes. Surgery remains the best option for more severe scars, other scars can be treated with the advance development of lasers for dermatological use. Treatment of scars with laser has steadily grown, giving both patients and physicians more flexibility to determine the best method of treatment.